Alex Profiled in MIT News
Jul 22, 2022
Read Alex’s new profile in MIT News here.

The Shalek Lab develops and applies broadly applicable experimental and computational platforms to understand and engineer immune responses in tissues. We employ a comprehensive, five-step approach, building innovative methodologies and leveraging them with partners around the world to facilitate deeper, more mechanistic inquiry into how cells drive tissue-level behaviors across the spectrum of human health and disease.
 Biology
Biology
 Cell Atlas
Cell Atlas
 Genomics
Genomics
 Immunology
Immunology
 Infectious Disease
Infectious Disease
 Microbiology
Microbiology
 Alex K. Shalek
Alex K. Shalek
 Conner Kummerlowe
Conner Kummerlowe
 Constantine Tzouanas
Constantine Tzouanas
 José Ordovas-Montañes
José Ordovas-Montañes
 Marc Wadsworth II
Marc Wadsworth II
 Samira Ibrahim
Samira Ibrahim
 Sarah Nyquist
Sarah Nyquist
 Travis Hughes
Travis Hughes
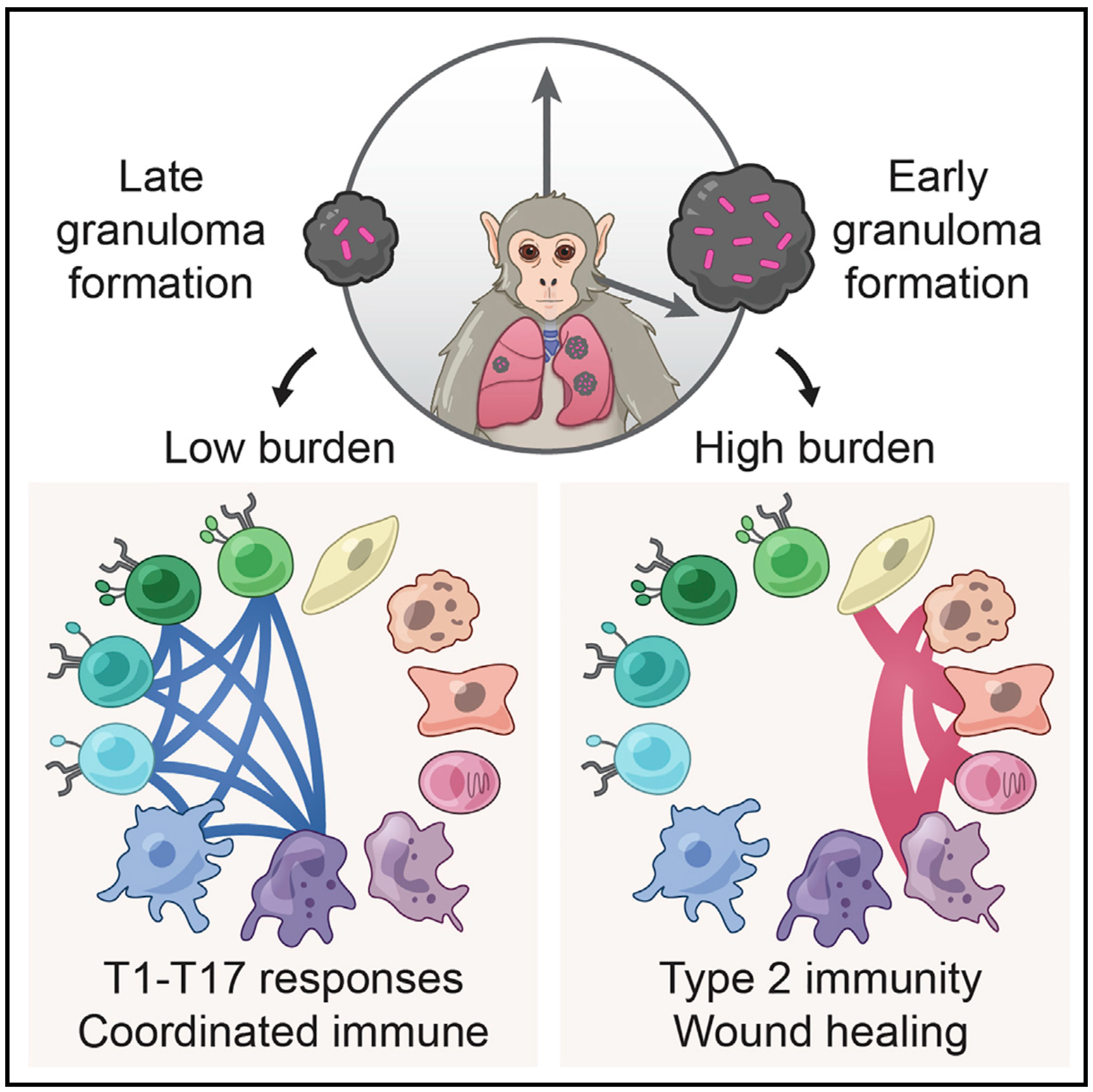
We integrate PET and CT imaging, scRNA-seq, and measures of bacterial clearance on TB granulomas from cynomolgus macaques to identify cellular features and programs associated with bacterial control and persistence of granulomas.
 Cancer
Cancer
 Computational Methods
Computational Methods
 Genomics
Genomics
 Immunology
Immunology
 Medicine
Medicine
 R&D
R&D
 Technology
Technology
 Alex K. Shalek
Alex K. Shalek
 Andrew Navia
Andrew Navia
 Jennyfer Galvez-Reyes
Jennyfer Galvez-Reyes
 Nolawit Mulugeta
Nolawit Mulugeta
 Peter Winter
Peter Winter
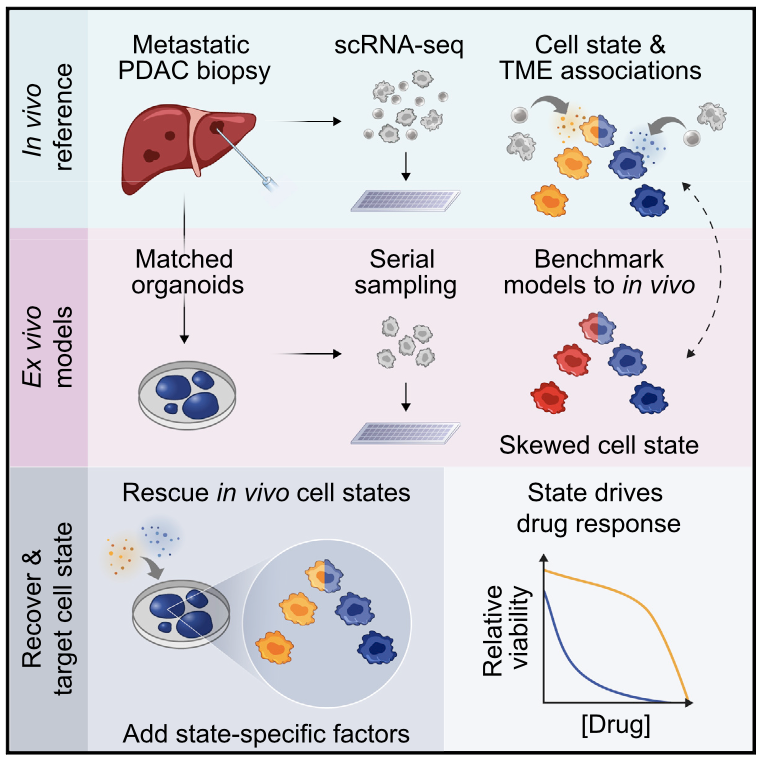
We profile metastatic biopsies and matched organoids to show that cancer cell state influences, and can be manipulated to shape, therapeutic response in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
 Biology
Biology
 Cell Atlas
Cell Atlas
 Computational Methods
Computational Methods
 Genomics
Genomics
 Immunology
Immunology
 Infectious Disease
Infectious Disease
 Alex K. Shalek
Alex K. Shalek
 Andrew Navia
Andrew Navia
 Carly Ziegler
Carly Ziegler
 Josh Bromley
Josh Bromley
 José Ordovas-Montañes
José Ordovas-Montañes
 Micayla George
Micayla George
 Riley Drake
Riley Drake
 Vincent Miao
Vincent Miao
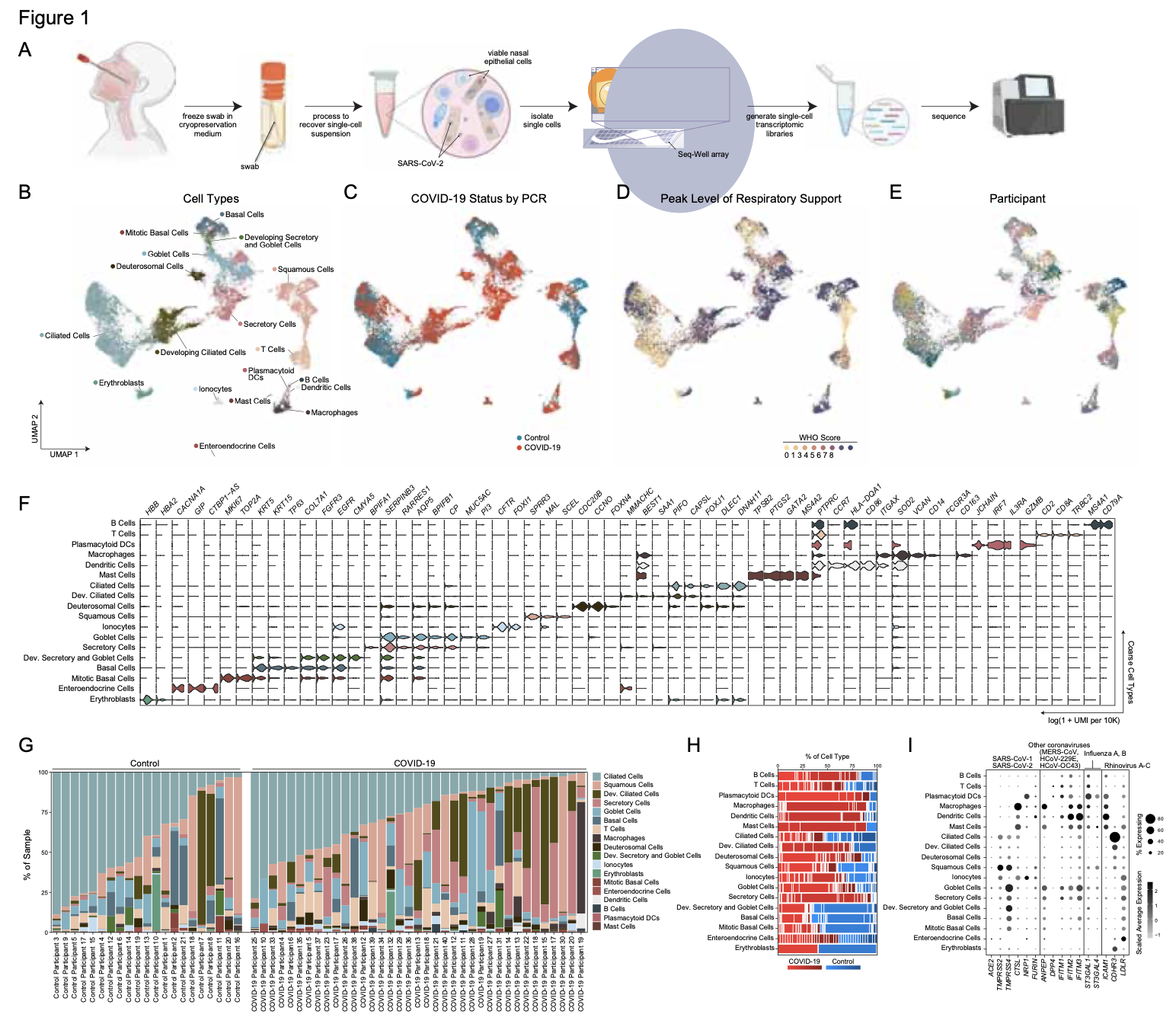
We analyze the nasopharyngeal cellular landscape of individuals with COVID-19, identifying putative initial target cells of SARS-CoV-2. Further, we find a blunted epithelial anti-viral response is correlated with the development of severe disease.
Jul 22, 2022
Read Alex’s new profile in MIT News here.
May 10, 2022
Check out the preview of our recent paper on TB granulomas here.
Mar 18, 2022
Listen to Alex Shalek on the Bioinformatics CRO Podcast Hear Alex talk about the Shalek Lab’s multi-disciplinary approach to answering some of science’s toughest and complex questions.